A Novel Route to Arylacetones via a Masked alpha-Acylcarbonium Intermediate
Shimon Shatzmiller, Ramy Lidor, Eytan Shalom and Eliezer Bahar
J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 795 (1984)The Ag+ induced aromatic substitution reaction of bromoacetone O-methyloxime is described.Abstract:
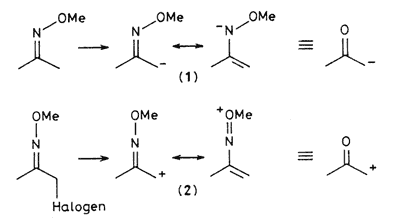
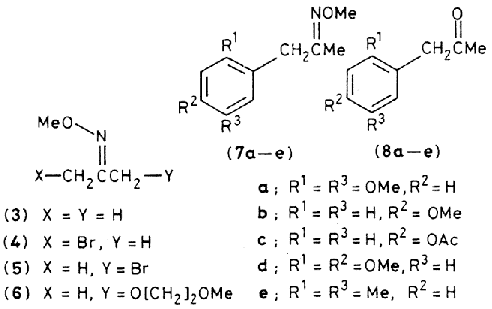
Oxime ethers can be efficiently metallated at the alpha-carbon atoms and the derived enolate equivalents (1) can then participate in a variety of useful C-C bond forming reactions. 1 The alpha-carbon might also support a positive charge [i.e. (2)] stabilized by n-type electron delocalization from the oxime group, and this cation could act as a synthetic equivalent of an l-acylcarbonium ion 2. In this communication we describe a method for the conversion of oxime ethers into functionalized ketones using reactive intermediates of type (1) or (2), employing acetone O-methyloxime as a model compound.Example 1:Litiation of acetone O-methyloxime (3) was achieved with 1.2M solution of
nBuLi in THF-hexane in 5 min at –65°C. Addition of lithiated (3) to molecular bromine in THF at –65°C over 15 min resulted in the formation of the Z-bromo-oxime ether, (4). Isomerization of (4) in CHCl
3-HBr gave the thermodynamically favored E-isomer. (5)
+ The halogen atom could be exchanged for alkoxy by treatment of (5) with 1.1eq. of MeO[CH
2]
2Ona in THF for 12hr to (6) in 88% yield.
The bromo-oxime ethers (4) and (5) were also converted into a reactive intermediate of type (2) which reacted in aromatic substitution reactions. Addition of 10mmol of either (4) or (5) in 20 ml of dry DCE to a solution of 10 mmol of AgBF
4 and 10mmol of the aromatic compound in 20ml of DCE at 25°C followed by efficient stirring in the dark for 18hr and then work-up with a 10% KCN-H
2 solution gave good (82-91%) yields of the aromatic substitution products (7a-e)
+ as the E-isomers. Acid treatment of (7a-e) (HCl-H
2O-MeOH 1:5:5) for 10 hrs at 65°C and distillation gave the corresponding arylacetones (8a-e) in high (90%) yield.
 References:
References:
1. V. Jaeger. H. Grund, and W. Schwab, Agnew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 1979, 18, 78; S. Shatzmiller and R. Lidor, JACS 1981, 103, 5916.
2. J.-P. Begue and M. Charpentier-Morize, Acc. Chem. Res. 1980, 13, 207.
3. G. J. Karbatsos and N. His Tetrahedron 1967, 23, 1079.
4. S. Shatzmiller, P. Gygax, D. Hall and A. Eschenmoser. Helv. Chim. Acta. 1973, 56, 2961
+ The geometry of the oxime ether moiety was elucidated on the basis of the chemical shift of the ketone Me group in the
2Hn.m.r. spectrum (CCl
4) e.g. the methyl hydrogens resonate at 2.01 in (4) but in (5) they are at 1.96. In (6), it is at 1.79 (E-isomer having 1.91) for (7a-e) the resonances are at 1.71, 1.70, 1.70, 1.71 and 1.74 respectively. Whereas the corresponding Z-isomers are at 1.75, 1.73, 1.74, 1.75 and 1.76 respectively. (see also Ref. 3).